投影变换(Projection Transformation)
在图形学中,常见2种投影变换:正交投影变换(Orthographic projection)、透视投影变换(Perspective projection)。
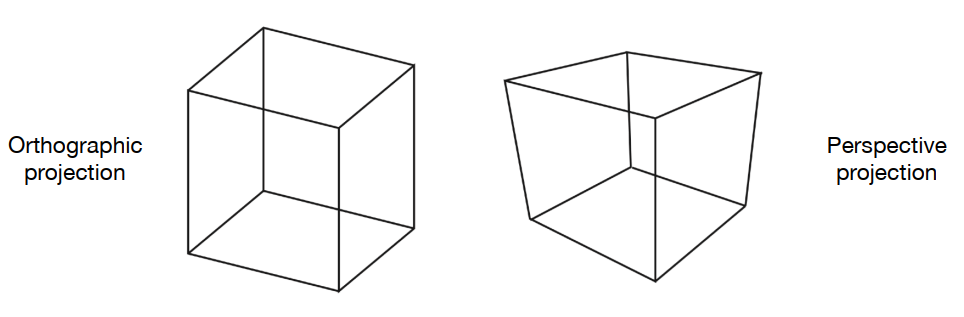
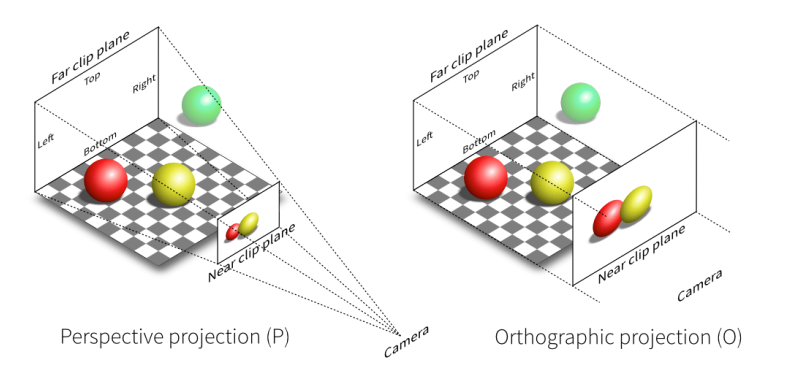
投影到相机平面的区别:透视投影和人眼看到的一致,满足近大远小;正交投影则不满足,如下图所示
正交投影变换(Orthographic Projection)
在空间内,选取一个区域(由6平面near-far-left-right-top-bottom包围区域)(Cuboid),将区域中心移至原点,再将区域内的点缩放到\(Cube[-1,1]^3\)标准(canonical)区域。过程如下图所示:
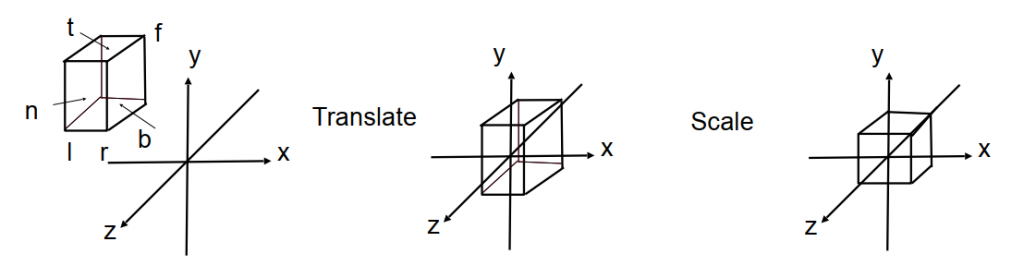
写成矩阵形式有 \(M_{ortho}=\begin{pmatrix} \frac{2}{r-l} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \frac{2}{t-b} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \frac{2}{n-f} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & -\frac{r+l}{2} \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -\frac{t+b}{2} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -\frac{n+f}{2} \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\end{pmatrix}\)
透视投影变换(Perspective Projection)
在欧氏几何中,两条平行直线用不相交。然而在我们眼睛所看到的透视投影中,2条很远平行的铁轨,在远处近乎交于一点,物体近大远小。
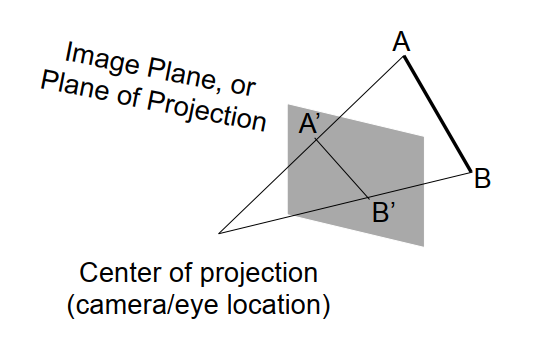
同正交投影类似的,我们也选取一块区域,不同的是这个区域并不是一个Cuboid,而是一个截锥体(Frustum)。如下图所示:
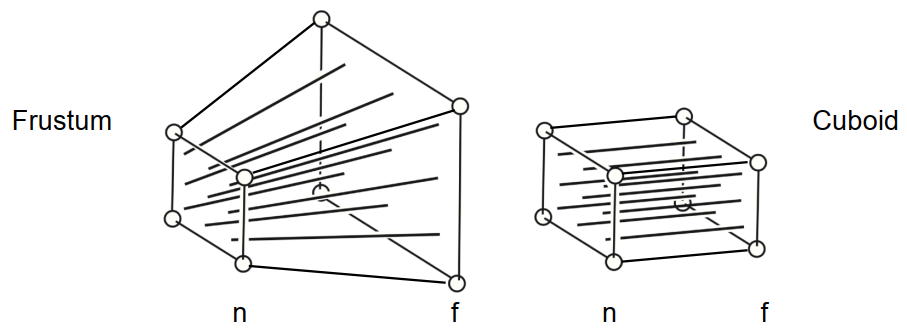
接下来只需要把这个截锥体通过变换,挤压(Squish)成Cuboid。Cuboid内的每一点按照Z轴(相机看向垂直Near,到Far平面的方向)前后排序,\((x,y)\)为Near平面的坐标,就可将三维空间的点投影在二维的平面中。
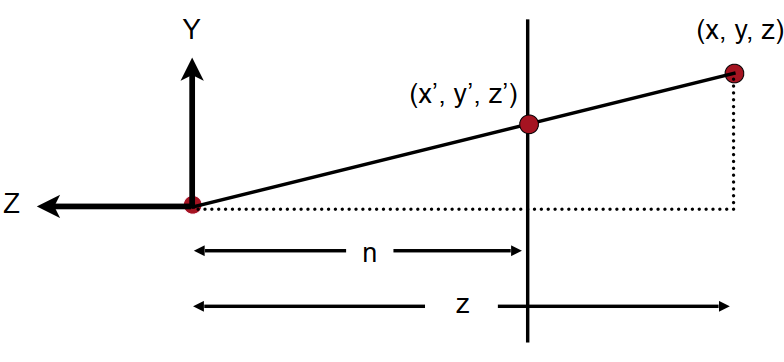
记Near平面的点为\((x’,y’,z’)\),如上图,x’和y’可通过三角形相似求得:\(\begin{cases} x’ = \frac{n}{z}x \\ y’ = \frac{n}{z}y \end{cases}\)
矩阵表达 \(\begin{pmatrix}x’ \\ y’\\ z’\\ 1\end{pmatrix} = M_{presp \to ortho}\begin{pmatrix}x \\ y\\ z\\ 1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} \frac{n}{z}x \\ \frac{n}{z}y\\ ?\\ 1\end{pmatrix}\) ,由齐次坐标点的定义有 \(\begin{pmatrix} \frac{n}{z}x \\ \frac{n}{z}y\\ ?\\ 1\end{pmatrix} == \begin{pmatrix} nx \\ny\\ ?\\ z\end{pmatrix}\)。
进一步,我们可以得到 \(M_{presp \to ortho} = \begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\ ? & ? & ? & ? \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{pmatrix} \)
由截锥体映射到Cuboid,满足:
Near平面上的点经过变换,坐标不变。\(\begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} nx \\ ny \\ ? \\ z\end{pmatrix}\),带入点 \((x,y,n)\) 有(齐次坐标点) \(\begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ n \\ 1\end{pmatrix}==\begin{pmatrix} nx \\ ny \\ n^2 \\ n\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} nx \\ ny \\ ? \\ n\end{pmatrix} \Rightarrow ?=n^2\)
进一步 \(\begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\ Q & W & A & B \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}x \\ y \\ n \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}nx \\ ny \\ n^2 \\ n \end{pmatrix} \Rightarrow An+B=n^2, Q=W=0\)
Far平面上的点经过变换,Z不变。
带入点 \((0,0,f)\) 有(齐次坐标点) \(\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ f \\ 1\end{pmatrix}==\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ f^2 \\ f\end{pmatrix} \Rightarrow \begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & A & B \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ f \\ 1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ f^2 \\ f\end{pmatrix}\Rightarrow Af+B=f^2\)
求得 \(\begin{cases} An+B=n^2 \\ Af+B=f^2\end{cases}\Rightarrow \begin{cases} A=n+f \\ B=-nf\end{cases} \Rightarrow M_{presp \to ortho} = \begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & n+f & -nf \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{pmatrix}\)
最后有 \(M_{presp} = M_{ortho}M_{presp \to ortho}\),得到了透视投影变换矩阵。
